Flux Administration and Logs
In the following
{org}is the name of your Arraylake organization{repo}is the name of the Repo{branch|commit|tag}is the branch, commit, or tag within the Repo to use to fulfill the request{path/to/group}is the path to group within the Repo that contains anxarrayDataset{protocol}is one of the supported protocols (e.g.edr,wms,dap).
Services
services are activated at an organization level, not per repo. Every service has a Deployment Name which is used to identify the service in the URL. By default, the deployment name is the same as the service type name. Deployment names must be unique and multiple services may be enabled at the same time for each protocol. This is typically useful for isolating testing and production environments.
These services can be managed in the web app, the CLI, or in the Python client:
Using the web app
To manage what services are active, whether or not they are public, and to view logs navigate to https://app.earthmover.io/{org}/settings/services. No services are enabled automatically; they must be explicitly turned on before use.
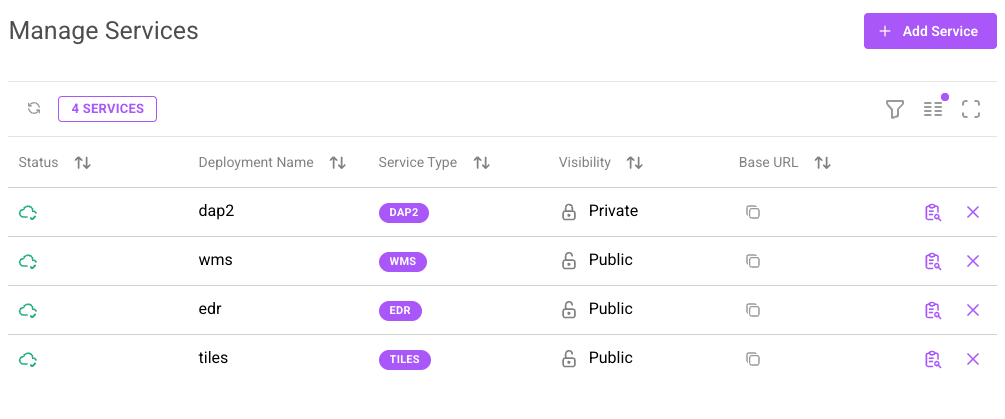
The organization services page
Enable a Service
Use the Add Service button to create a new service.
Services can either be open to the public (as in earthmover-public which is used in all the examples) or private, in which case they will require Authentication to access. You can also specify a custom deployment name for each service created.
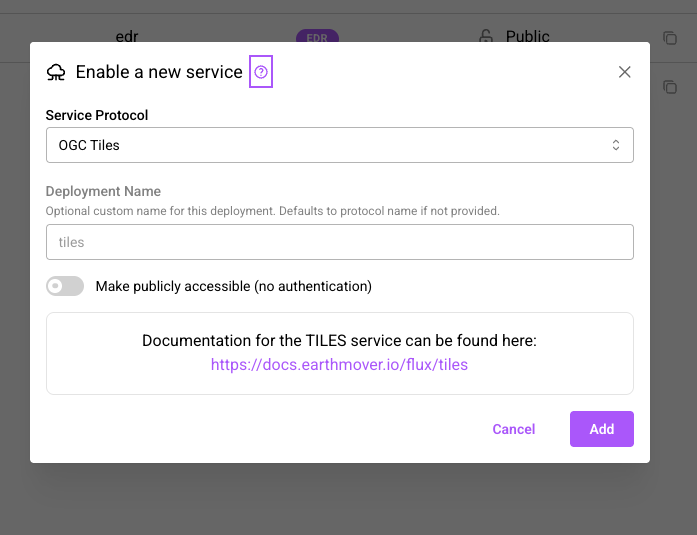
The create service modal
Disable a Service
Use the Disable button to disable a service.
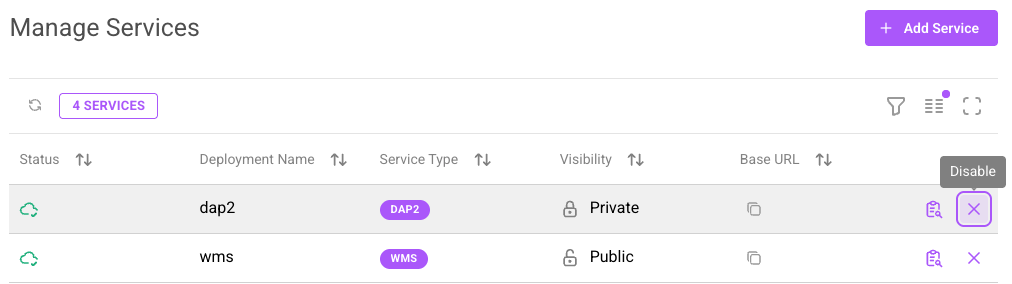
The disable service button
Using the CLI
You can also manage services via the arraylake command line client.
Service Status
al compute list {org}
Enable a Service
By default the service is only accessible to those with access to the Repo being queried. Provide the --is-public flag to open access to all users without authentication. For more information, see the Authentication page. A custom Deployment name can also be specified by using the --deployment-name argument.
Custom deployment names are only supported with arraylake>=0.29.0.
al compute enable {org} {protocol}
Check Service Status
al compute status {org} {service_name}
Disable a Service
To disable choose the appropriate service_name from the output of al compute list {org}.
al compute disable {org} {service_name}
Using the Client
services can also be managed via the arraylake python SDK. Use the Client to get the control interface for an organizations services:
from arraylake import Client
client = Client()
services = client.get_services("earthmover-public")
Service Status
services.list_enabled()
Enable a Service
Like using the CLI or Web app, you can create services and control the deployment name and whether the service is public or not.
Custom deployment names are only supported with arraylake>=0.29.0.
services.enable("tiles", deployment_name='public-tiles', is_public=True)
Check Service Status
services.get_status("{service_name}")
Disable a Service
To disable choose the appropriate service_name from the output of services.list_enabled().
services.disable("{service_name}")
Logs
Running flux services generate logs. These can be viewed in the web app or via the CLI. You can use the logs to analyse usage or help debug problems.
Using the web app
To view the flux logs in the web app, navigate to the Organization Settings page, then the Services tab. Then click the Logs button next to the service whose logs you want to see.
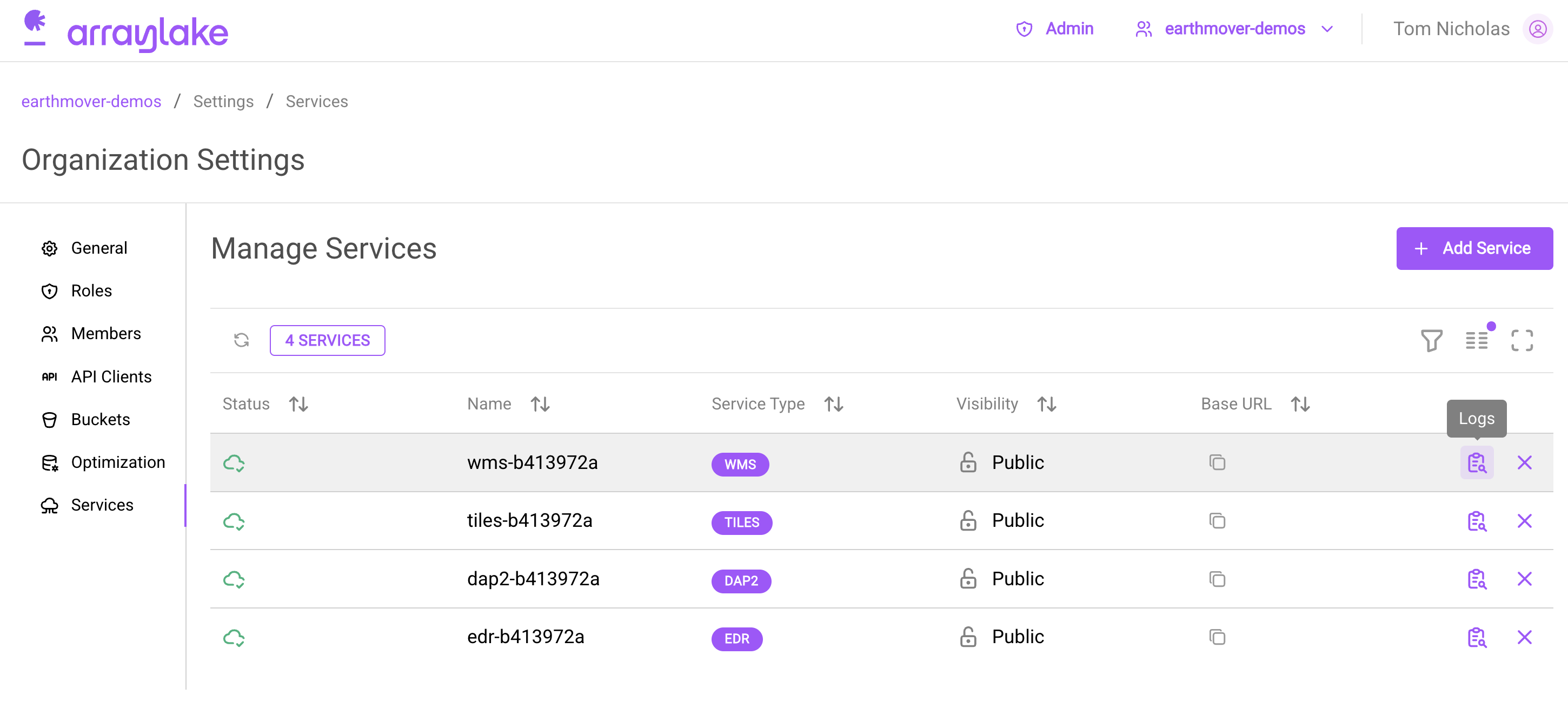
Button to view Flux logs.
This should show some logs:
Example logs from a Flux Service.
You can view the latest logs, view specific time windows, or follow live logs as they appear.
Using the CLI
You can also view flux logs via the arraylake CLI:
al compute logs {org} {service_name}
For example
al compute logs earthmover-demos edr-b413972a
✓ Getting service logs for edr-b413972a...succeeded
2025-08-21T08:12:30.157419663Z | [INFO] 10.0.9.176:39080 - "GET
/v1/services/edr/earthmover-demos/dyanmical-gfs-analysis/main/edr/position?coords=POINT(5.669308322197139%2051.913490501057254)&time=2015-05-01T0
0:00:00/2015-06-01T00:00:00&f=cf_covjson¶meter-name=temperature_2m&f=cf_covjson HTTP/1.1" 200
2025-08-21T08:12:52.354997634Z | [INFO] 10.0.9.176:47256 - "GET
/v1/services/edr/earthmover-demos/dyanmical-gfs-analysis/main/edr/position?coords=POINT(86.70079407664105%2029.937047793387052)&time=2015-05-01T0
0:00:00/2015-06-01T00:00:00&f=cf_covjson¶meter-name=temperature_2m&f=cf_covjson HTTP/1.1" 200
2025-08-21T08:13:59.142135Z | [INFO] 10.0.66.178:39184 - "GET
/v1/services/edr/earthmover-demos/dyanmical-gfs-analysis/main/edr/position?coords=POINT(-1.3354108407841068%207.489843848990361)&time=2015-05-01T
00:00:00/2015-06-01T00:00:00&f=cf_covjson¶meter-name=temperature_2m&f=cf_covjson HTTP/1.1" 200
2025-08-21T08:14:00.029393771Z | [INFO] 10.0.66.178:47754 - "GET
/v1/services/edr/earthmover-demos/dyanmical-gfs-analysis/main/edr/position?coords=POINT(13.760277782786034%201.1747459774573912)&time=2015-05-01T
00:00:00/2015-06-01T00:00:00&f=cf_covjson¶meter-name=temperature_2m&f=cf_covjson HTTP/1.1" 200
2025-08-21T08:14:06.567584468Z | [INFO] 10.0.66.178:47762 - "GET
/v1/services/edr/earthmover-demos/dyanmical-gfs-analysis/main/edr/position?coords=POINT(-43.272690538306165%2065.3366654982585)&time=2015-05-01T0
0:00:00/2015-06-01T00:00:00&f=cf_covjson¶meter-name=temperature_2m&f=cf_covjson HTTP/1.1" 200
Various CLI flags allow you to follow logs as they appear (--follow), fetch only the most recent lines of logs (--tail), or fetch only logs between certain times (--since and --until).
See all the available CLI flags with arraylake compute logs --help.
Using the Client
To access logs from the Python client, first obtain the services object as shown in the Using the Client section above.
services.get_logs("{service_name}")
You can specify the tail, since, and until parameters to fetch logs based on your requirements.