Azure Blob Storage

Azure Blob Storage is Microsoft Azure's object storage solution for the cloud, optimized for storing massive amounts of unstructured data. In Arraylake, you can use Azure Blob Storage as the storage location for your organization.
Azure uses the term container to refer to the organizational unit that holds blobs (objects) within a storage account. This is equivalent to what AWS calls a bucket and what GCS calls a bucket. In Arraylake, we use the AWS-native term "bucket" across all storage providers for consistency, but when working with Azure, your BucketConfig points to an Azure container.
To use Azure Blob Storage with Arraylake:
-
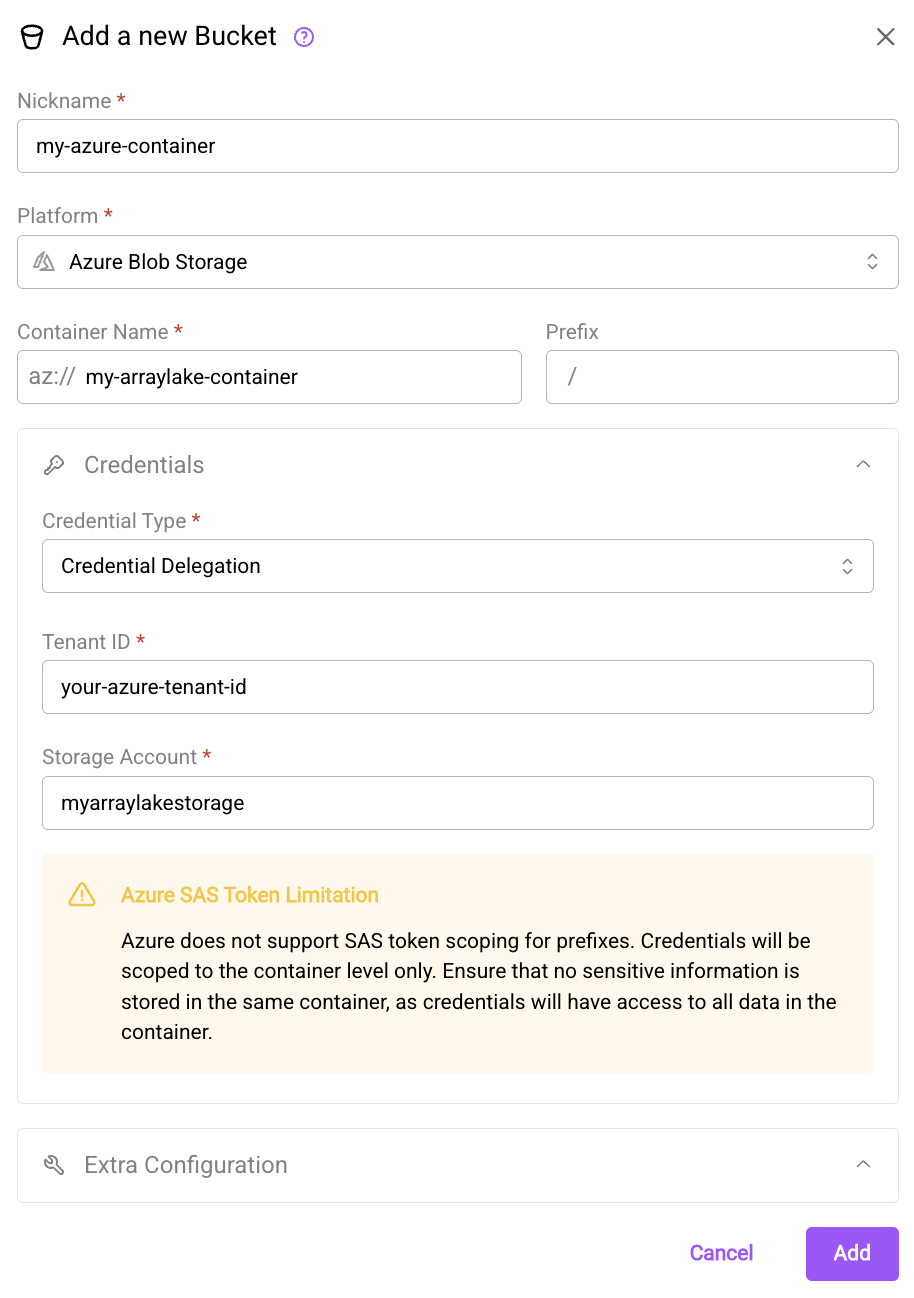
Create a new storage account and container (Azure docs). For example, the storage account could be named
myarraylakestorageand the container could be namedmy-arraylake-container. -
Create a new
BucketConfigto store the configuration for this container using either the Arraylake Python client or web app:
Azure Blob Storage supports credential delegation using user delegation SAS tokens!
- Web App
- Python
Add a new Azure Blob Storage Container
from arraylake import Client
client = Client()
client.create_bucket_config(
org="earthmover",
nickname="my-azure-container",
uri="az://my-arraylake-container",
auth_config={
"method": "azure_credential_delegation",
"tenant_id": "your-azure-tenant-id",
"storage_account": "myarraylakestorage"
}
)
That's it! You're ready to create a Repository! 🎉
Understanding Azure Delegated Credentials
Arraylake uses Azure AD (Entra ID) authentication to generate temporary, container-scoped SAS (Shared Access Signature) tokens for your Azure storage. These credentials:
- Have a lifetime of 1 hour
- Are scoped at the container level (not prefix level, unlike AWS S3)
- Use user delegation keys for enhanced security
For detailed setup instructions, see the Azure Blob Storage section in the Manage Storage guide.